On a typical Linux host, rolling back a configuration in WildFly can be as simple as copying a backup of the configuration XML file back into place. However, working within the constraints of a secured virtual appliance (vApp) presents a unique challenge: the primary service ID often lacks write access to critical files under the WildFly deployment.
When faced with this limitation, administrators may feel stuck. What options do we have? Thankfully, WildFly’s jboss-cli.sh process provides a lifeline for configuration management, allowing us to take snapshots and reload configurations efficiently. See the bottom of this blog if you need to create a user for jboss-cli.sh usage.
Why Snapshots are necessary for your sanity
WildFly snapshots capture the server’s current configuration, creating a safety net for experimentation and troubleshooting. They allow you to test changes, debug issues, or introduce new features with confidence, knowing you can quickly restore the server to a previous state.
In this guide, we’ll explore a step-by-step process to test and restore configurations using WildFly snapshots on the Symantec IGA Virtual Appliance.
Step-by-Step: Testing and Restoring Configurations

Step 1: Stamp and Backup the Current Configuration
First, optionally you may add a unique custom attribute to the current `standalone.xml` (ca-standalone-full-ha.xml) configuration, if you don’t already have a delta to compare. This new custom attribute acts as a marker, helping track configuration changes. After updating the configuration, take a snapshot.
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:remove()"
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:add(value='v1.0.20241114-Alan-was-here')"
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:read-resource"
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command=":take-snapshot"Step 2: Modify the Configuration for Testing
Simulate a change by updating the custom attribute. Validate the update with a read query to confirm the changes are applied. To be safe, we will remove the attribute and re-add with a new string that is different.
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:remove()"
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:add(value='v1.0.20241114-Alan-was-here_v2')"
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:read-resource"Step 3: Review Available Snapshots
List all available snapshots to identify the correct rollback point.
You can use the `:list-snapshots` command to query snapshots and verify files in the snapshot directory.
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command=":list-snapshots"
ls -l /opt/CA/wildfly-idm/standalone/configuration/standalone_xml_history/snapshot/Step 4: Reload from Snapshot
Once you’ve identified the appropriate snapshot, use the `reload` command to roll back the configuration. This is the
Monitor the process to ensure it completes successfully, then verify the configuration.
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command=":reload(server-config=/standalone_xml_history/snapshot/20241114-232053024ca-standalone-full-ha.xml)"
tail -F /opt/CA/wildfly-idm/standalone/log/wildfly-console.log
/opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/jboss-cli.sh --connect --user=jboss-admin --password=Password01! --timeout=90000 --command="/system-property=custom.config.version:read-resource"Adding a WildFly Admin User for Snapshot Management
Before you can execute commands through WildFly’s `jboss-cli.sh`, you’ll need to ensure you have a properly configured admin user.
If an admin user does not already exist, you can create one with the following command:
sudo /opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/add-user.sh -m -u jboss-admin -p Password01! -g SuperUser
- **`-m`**: Indicates the user is for management purposes.
- **`-u jboss-admin`**: Specifies the username (`jboss-admin` in this case).
- **`-p Password01!`**: Sets the password for the user.
- **`-g SuperUser`**: Assigns the user to the `SuperUser` group, granting necessary permissions for snapshot and configuration management.You can have as many jboss-cli.sh service IDs as you need.
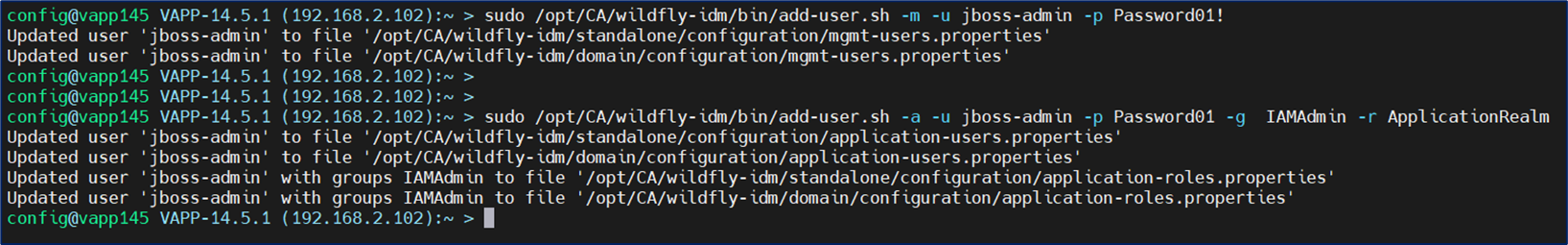
Please note, this Wildfly management service ID is not the same as the Wildfly application service ID, that is needed for the /iam/im/logging_v2.jsp access. Which requires the -a switch and the group of IAMAdmin
sudo /opt/CA/wildfly-idm/bin/add-user.sh -a -u jboss-admin -p Password01! -g IAMAdmin -r ApplicationRealmIf your logging_v2.jsp page is not displaying correct, there is simple update to resolve this challenge. Add the below string to your /opt/CA/VirtualAppliance/custom/IdentityManager/jvm-args.conf file.
-DLog4jContextSelector=org.apache.logging.log4j.core.selector.BasicContextSelectorConsider the above as good practice before any major update or upgrade. We can work with you to manage your environment.
